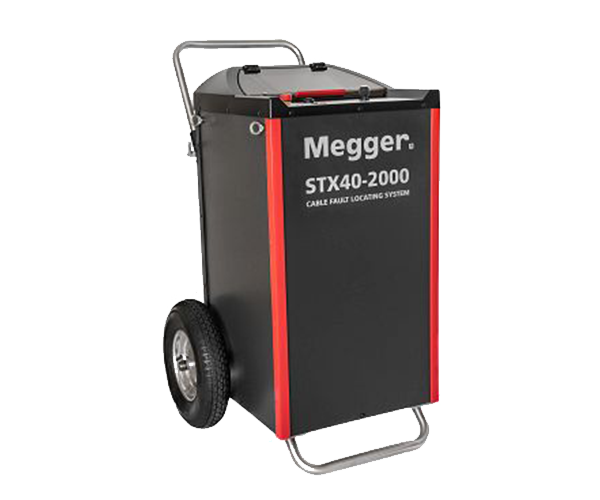
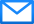
■ Outdoor unit with exceptional all-terrain mobility:Lightweight, rainproof, optimised center of gravity, large pneumatic tires, adjustable handlebar, IP 43 rating, 119 kg (262 lbs)
■ Bright, sunlight readable 10.1” color display
■ Automatic operating mode selection and execution via software-controlled HV motor switches
■ To identify different types of faults: Insulation test up to 20 kV and 650 MΩ
■ DC test (DC hipot) up to 40 kV, with automatic voltage breakdown detection and ramp function
■ Built-in and functionally integrated Radar/TDR as well as ARM, ICE and DECAY prelocation methods
■ Surging (Thumping) at 8/16/32 kV with 2,000 J Optionally available: additional 4 kV stage with 1,100 J
■ High frequency burn mode with up to 40 kV DC and up to 850 mA, for improved fault conversion performance over conventional burn-down units with burn transformer
■ Field-ready design, IP 43
■ Software-based user interface with single “turn & click” rotary knob control
■ Fully automatic operation of all modes via motorised switching
■ Physically and functionally integrated Radar/TDR (Teleflex® RDR)
■ Prelocation methods: ARM, ICE and DECAY
■ Best Picture Multishot technology:32 HV fault traces per ARM shot and instant display of the best trace
■ DC test and burning up to 40 kV, surging (thumping) up to 32 kV, delivers 2,000 J
■ Safety interlocks for monitoring of station earth and touch potentials (F-U), as well as earth connections (F-Ohm) STX40-P High-end portable standalone cable fault location unit Extensive selection of fault finding technologies:In addition to Radar, STX 40 comes with a comprehensive set of HV prelocation methods to find the distance to the fault.
■ Inductive ARM Best Picture Multishot: The Arc Reflec�tion Method overlays and compares a low voltage refer�ence trace with 32 high voltage fault traces [Multishot]. Those 32 consecutive measurements are analysed, and the best one is automatically displayed to the operator [Best Picture]. An inductive filter provides superior properties for arc ignition and arc stabilisation compared to less effective resistive filters.
■ ICE/Surge Pulse: After the fault has been ignited, the Impulse Current Decoupling method measures the current component of the initiated travelling wave. ICE is an alter�native to ARM and suitable for longcables, PILC cables, for wet faults and for faults which are not chargeable.
■ DECAY: After the fault has been ignited, the Voltage Decoupling method measures the voltage component of the initiated travellingwave. Decay is an alternative to ARM and ICE, and suitable for long cables, HV trans�mission cables, faults which are chargeable as well as high resistance faults with a veryhigh breakdown voltage.
■ IFL: Mode for Intermittent Fault Location. By repeatedly capturing radar traces and visualising the area between curves, IFL is able to find unsteady, erratic faults which may have quickly changing characteristics. This is benefi�cial when working on street lighting installations or similar LV cables.